Install WordPress 4.1.1 on Fedora 21/20, CentOS/RHEL 7/6.6/5.11
Table of Contents

This is guide, howto install WordPress 4.1.1 with Nginx or Apache on Fedora 21/20/19, CentOS 7/6.6/5.11 and Red Hat (RHEL) 7/6.6/5.11 servers. WordPress needs web server with PHP and MariaDB or MySQL database. This guide uses Apache web server with PHP 5.6 or Nginx web server with PHP 5.6 (PHP-FPM) and MariaDB 10/5.5 database server or Mysql 5.6 database server.
If you want to install WordPress with Apache then use a – [Apache] sections and if you want install WordPress with Nginx then use b – [Nginx] sections.
1. Install Needed Web and Database Servers⌗
[Apache]
1.1a Install the whole LAMP environment with following guide⌗
LAMP (Linux/Apache/MySQL/PHP) on Fedora, CentOS/Red Hat (RHEL)
[Nginx]
1.1b Install the whole LEMP environment with following guide⌗
LEMP (Linux/Nginx/MySQL/PHP) on Fedora, CentOS/Red Hat (RHEL)
OR
[Apache]
1.2a Install just MariaDB or MySQL and Apache with PHP using following guides⌗
- Install MariaDB 10/5.5 on Fedora, CentOS, Red Hat (RHEL)
- Install MySQL 5.6 on Fedora, CentOS, Red Hat (RHEL)
- Install Apache (httpd) and PHP 5.6 on Fedora, CentOS, Red Hat (RHEL)
[Nginx]
1.2b Install just MariaDB or MySQL and Nginx with PHP (PHP-FPM) using following guides⌗
- Install MariaDB 10/5.5 on Fedora, CentOS, Red Hat (RHEL)
- Install MySQL 5.6 on Fedora, CentOS, Red Hat (RHEL)
- Install Nginx and PHP 5.6 (PHP-FPM) on Fedora, CentOS, Red Hat (RHEL)
2. Install WordPress 4.1.1 on Fedora 21/20/19, CentOS/Red Hat (RHEL) 7/6.6/5.11⌗
2.1 Change root user⌗
su -
## OR ##
sudo -i
2.2 Download WordPress 4.1.1 / latest⌗
cd /tmp
wget http://wordpress.org/latest.tar.gz
[Apache]
2.3a Untar/Extract Downloaded WordPress Package⌗
tar -xvzf latest.tar.gz -C /var/www/html
[Nginx]
2.3b Create needed directories, set permissions and untar/Extract Downloaded WordPress Package⌗
mkdir -p /srv/www/wordpress/public_html
mkdir /srv/www/wordpress/logs
tar -xvzf latest.tar.gz -C /srv/www/wordpress/public_html --strip-components=1
chown -R apache:apache /srv/www/wordpress
Note: I use apache user and group here, because PHP-FPM runs as apache default (apache Choosed to be able to access some dir as httpd). If you use some other user on your php-fpm conf then change this accordingly.
3. Create MariaDB/MySQL Database for WordPress⌗
3.1 Connect MariaDB/MySQL Database as root⌗
## localhost ##
mysql -h localhost -u root -p
## Remote server ##
mysql -h 10.0.0.15 -u username -p
3.2 Setup MariaDB/MySQL Database for WordPress⌗
## Create new user ##
CREATE USER wordpress@localhost IDENTIFIED BY "some_good_password_for_wordpress";
## Create new database ##
CREATE DATABASE wordpress_blog;
## Grant needed permissions ##
GRANT ALL ON wordpress_blog.* TO wordpress@localhost;
## Flush privileges ##
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
## Exit ##
exit
4. Setup WordPress⌗
[Apache]
4.1a Create Apache VirtualHost for WordPress⌗
This is simple VirtualHost setup for local usage. VirtualHost is not mandatory for WordPress installation.
Add following to /etc/httpd/conf.d/wordpress.conf file:
<virtualhost>
ServerAdmin test@test
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/wordpress
ServerName wordpress
# Logging
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/wordpress-error-log
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/wordpress-acces-log common
</virtualhost>
Restart Apache (httpd)
## Fedora 21/20/19 and CentOS/RHEL 7 ##
systemctl stop httpd.service
## CentOS/RHEL 6.6/5.11 ##
service httpd stop
## OR ##
/etc/init.d/httpd stop
[Nginx]
4.1b Create Nginx VirtualHost for WordPress⌗
Create sites-available and sites-enabled directories
mkdir /etc/nginx/sites-available
mkdir /etc/nginx/sites-enabled
Include sites-enabled
Add following lines to /etc/nginx/nginx.conf file, after “include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf” line (inside http block).
## Load virtual host conf files. ##
include /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/*;
Create Nginx wordpress virtual host file
Add following content to /etc/nginx/sites-available/wordpress file. This is basic Nginx virtual host config file for wordpress.
server {
server_name wordpress;
access_log /srv/www/wordpress/logs/access.log;
error_log /srv/www/wordpress/logs/error.log;
root /srv/www/wordpress/public_html;
location / {
index index.php;
}
# Disable favicon.ico logging
location = /favicon.ico {
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
}
# Allow robots and disable logging
location = /robots.txt {
allow all;
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
}
# Enable permalink structures
if (!-e $request_filename) {
rewrite . /index.php last;
}
# Handle php requests
location ~ \.php$ {
include /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
}
# Disable static content logging and set cache time to max
location ~* \.(js|css|png|jpg|jpeg|gif|ico)$ {
expires max;
log_not_found off;
}
# Deny access to htaccess and htpasswd files
location ~ /\.ht {
deny all;
}
}
Create symlink on sites enabled directory
cd /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/wordpress
Restart Nginx server
## Fedora 21/20/19 and CentOS/RHEL 7 ##
systemctl stop nginx.service
## CentOS/RHEL 6.6/5.11 ##
service nginx stop
## OR ##
/etc/init.d/nginx stop
4.2 Set wordpress pointing to localhost (or some other host)⌗
Add following to /etc/hosts file:
127.0.0.1 wordpress
[Apache]
4.3a Create wp-config.php⌗
cd /var/www/html/wordpress
cp wp-config-sample.php wp-config.php
[Nginx]
4.3b Create wp-config.php⌗
cd /srv/www/wordpress/public_html
cp wp-config-sample.php wp-config.php
4.4 Configure WordPress wp-config.php file⌗
Open wp-config.php with text editor.
Setup at following database settings (which was created in section 3.2)⌗
// ** MySQL settings - You can get this info from your web host ** //
/** The name of the database for WordPress */
define('DB_NAME', 'database_name_here');
/** MySQL database username */
define('DB_USER', 'username_here');
/** MySQL database password */
define('DB_PASSWORD', 'password_here');
/** MySQL hostname */
define('DB_HOST', 'localhost');
/** Database Charset to use in creating database tables. */
define('DB_CHARSET', 'utf8');
/** The Database Collate type. Don't change this if in doubt. */
define('DB_COLLATE', '');
Insert some unique data on following section⌗
define('AUTH_KEY', 'put your unique phrase here');
define('SECURE_AUTH_KEY', 'put your unique phrase here');
define('LOGGED_IN_KEY', 'put your unique phrase here');
define('NONCE_KEY', 'put your unique phrase here');
define('AUTH_SALT', 'put your unique phrase here');
define('SECURE_AUTH_SALT', 'put your unique phrase here');
define('LOGGED_IN_SALT', 'put your unique phrase here');
define('NONCE_SALT', 'put your unique phrase here');
Generate unique phrases using pwgen
Install pwgen:
yum install pwgen
Generate phreses with pwgen:
pwgen -sy 50
Output:
l_fO1Q6\P>yYfsWZ9BY7_jj;U2k&,'5do!;rR5L!~M]y_{]~me
lOVt"rJk.rqZRUXA)VNZHs@]A1W1Zzdcb?+4y5D4'5zCYy>5lI
m8)ab[9]JO$S_;\+u0Q>e~@:VZ|N!R{u#3\NZavWZv.caQ_?GU
bu}g.6=j,6/at-lm1u2S_K>3ckX=EeI~i$?0p]zD|pO((a{b1]
#-otVokEQz9+&M0hokkKL]l*BK|c5w}bFmUZ:|=v'B:"_u^LV7
z{N*`:~6IzgL%p;#j_:8)nReK|*Cdr%#e)"F-v_VKWahLi%p\t
C+to$qo~PTq8=BD0{jv?dJyiY(L;'2sW`CnW!4*#y>|#Xpa4TF
%BCO]d}[ag5ivSZz+[ER]sr@W}`*J6](jFtQ]h>,D<ma ai-4.lx7q="">FKN?#?HXLJXB(i
~dMJ[e"S}c4R>7^Q)vG{Uq-):e}4I+]zsM@h#sz*7{Bnk}oa(y
...
Then simply use these generated phrases on WordPress config file. Remember remove or replace all quotation marks.
Check/Setup following parameters if needed:⌗
// WordPress Database Table prefix
$table_prefix = 'wp_';
// WordPress Localized Language, defaults to English
define ('WPLANG', '');
// For developers: WordPress debugging mode
define('wp_DEBUG', false);
Save wp-config.php file!
This guide example wp-config.php could look following⌗
define('DB_NAME', 'wordpress_blog');
define('DB_USER', 'wordpress');
define('DB_PASSWORD', 'some_good_password_for_wordpress');
define('DB_HOST', 'localhost');
define('DB_CHARSET', 'utf8');
define('DB_COLLATE', '');
define('AUTH_KEY', 'l_fO1Q6\P>yYfsWZ9BY7_jj;U2k&,"5do!;rR5L!~M]y_{]~me');
define('SECURE_AUTH_KEY', 'lOVt"rJk.rqZRUXA)VNZHs@]A1W1Zzdcb?+4y5D4"5zCYy>5lI');
define('LOGGED_IN_KEY', 'm8)ab[9]JO$S_;\+u0Q>e~@:VZ|N!R{u#3\NZavWZv.caQ_?GU');
define('NONCE_KEY', 'bu}g.6=j,6/at-lm1u2S_K>3ckX=EeI~i$?0p]zD|pO((a{b1]');
define('AUTH_SALT', '#-otVokEQz9+&M0hokkKL]l*BK|c5w}bFmUZ:|=v"B:"_u^LV7');
define('SECURE_AUTH_SALT', 'z{N*`:~6IzgL%p;#j_:8)nReK|*Cdr%#e)"F-v_VKWahLi%p\t');
define('LOGGED_IN_SALT', '%BCO]d}[ag5ivSZz+[ER]sr@W}`*J6](jFtQ]h>,D<ma define="">7^Q)vG{Uq-):e}4I+]zsM@h#sz*7{Bnk}oa(y');
$table_prefix = 'wp_';
define ('WPLANG', '');
define('wp_DEBUG', false);
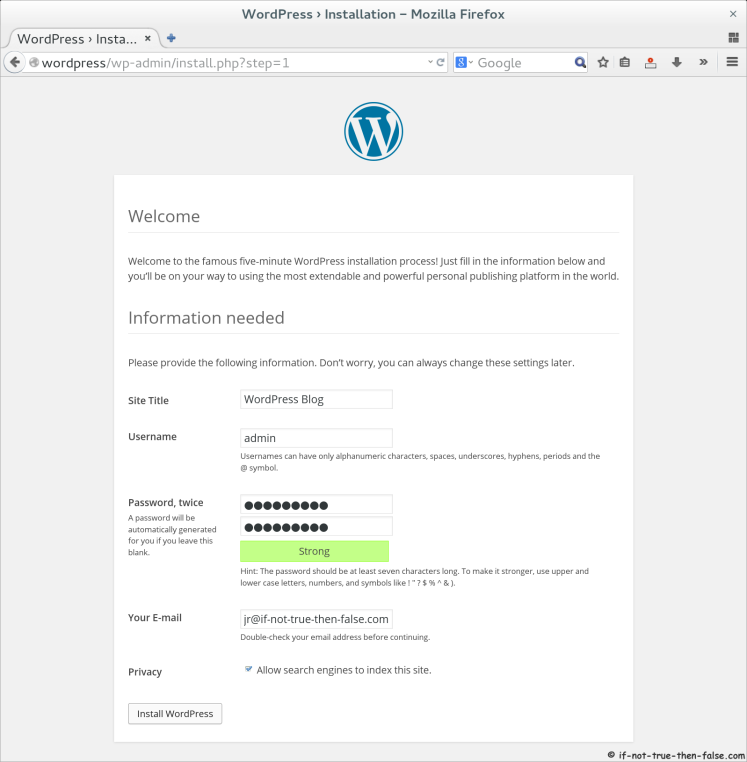
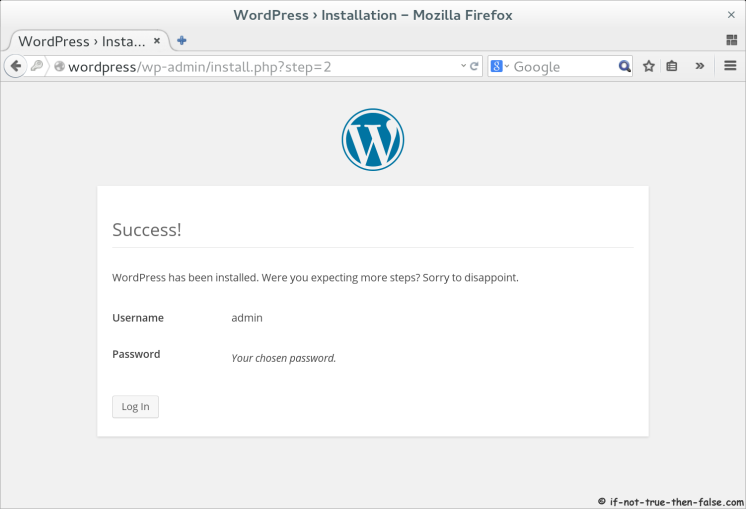
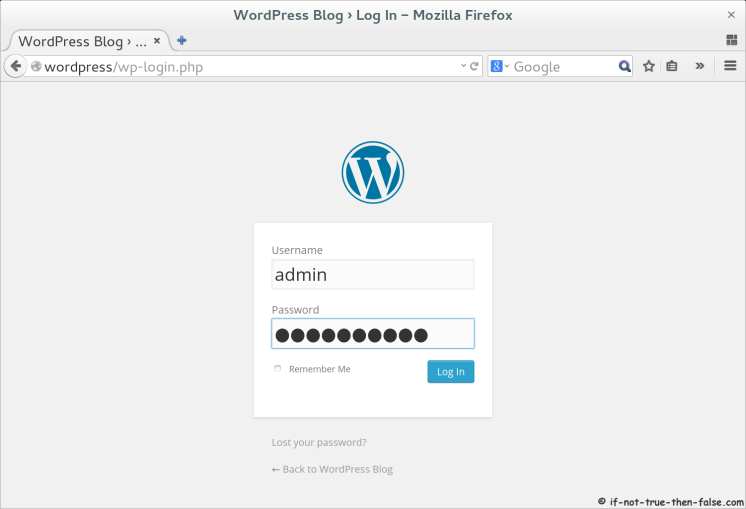
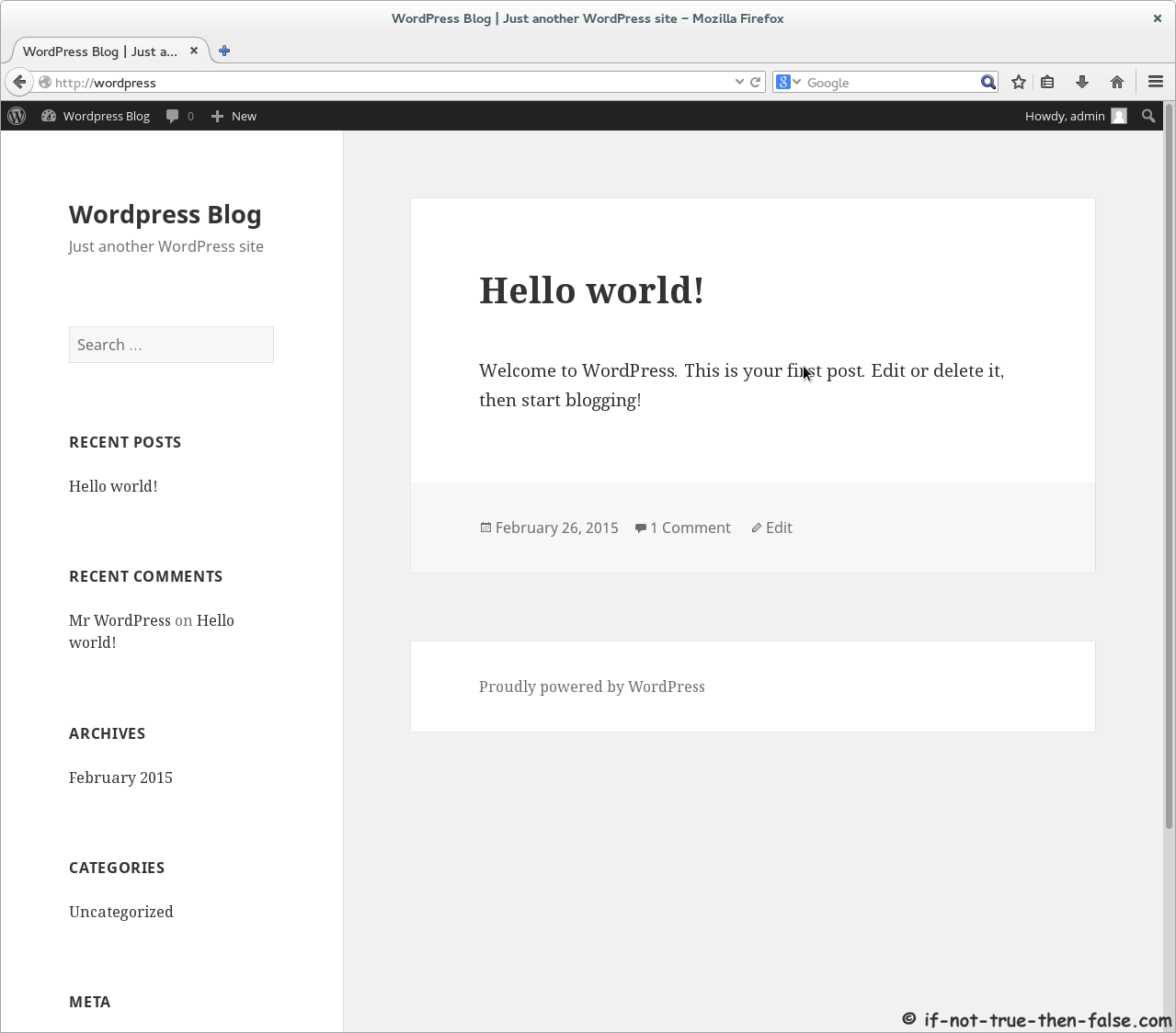
4.5 Finnish WordPress Configuration with Browser⌗
Open browser and Goto following address http://wordpress/.